Device implementation tutorial
←Tutorials · Index↑ · Controller implementation tutorial→
- Device implementation tutorial
This section covers the basis for quickly building an MS-05 / IS-12 device implementation.
Guidance
This section provides guidance in select focus areas required for device implementations.
For full definitions of models referred to in this document please check the IDL.
The basic device workflow follows the diagram below where individual steps are detailed in the following subsections.
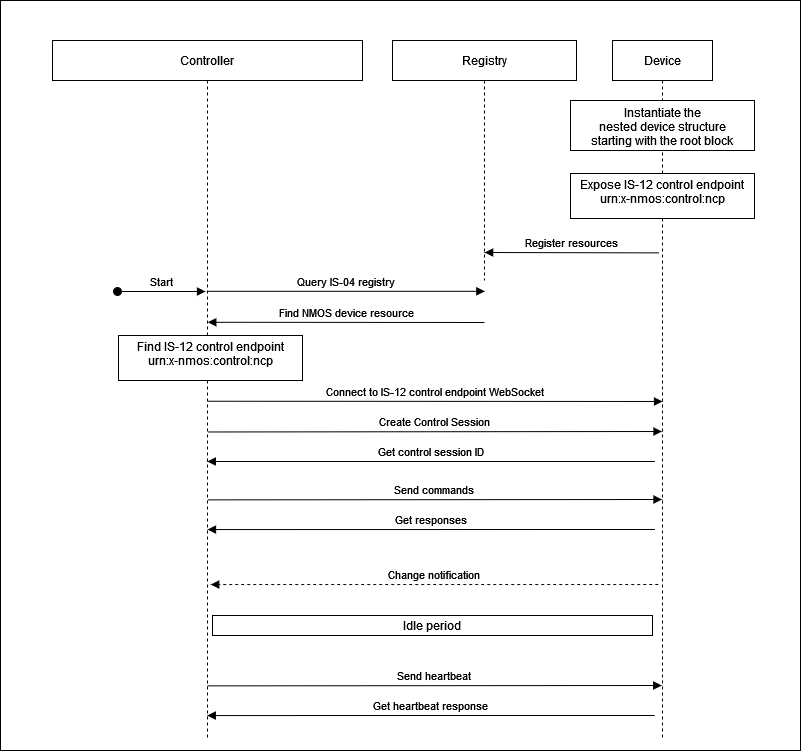 |
|---|
| Basic device sequence |
Modelling the control classes
As per the MS-05-02 specification all control classes must inherit from NcObject.
This base control class exposes important properties but also generic methods for getting and setting property values.
NcObject also defines the PropertyChanged event which is fundamental for subscriptions and notifications to work.
As per the MS-05-01 specification there are different types of identifiers which ultimately can be split into two categories:
- dynamic identifiers (object identifiers)
- persistent identifiers (roles, class identities and data type names)
 |
|---|
| Identities |
Block control classes
As per the MS-05-02 specification blocks are containers for other control classes.
All devices have at the very least a root block which is the top most block in the device tree. The root block has an oid of 1 and the role of root.
Control classes which are nested inside a block are advertised using descriptors in the members property (2p10) of NcBlock.
The members property in blocks enables tree discovery of the device structure.
Blocks are also useful for quickly finding a particular control class by using the search methods provided.
Manager control classes
As per the MS-05-02 specification managers are special classes which collate information which pertains to the entire device.
Typical managers included in the root block are:
- Device manager (holds general information about the device including product information and serial numbers)
- Subscription manager (offers means of subscribing to events thus enabling notifications)
- Class manager (offers means of class and data type discovery)
Worker control classes
As per the MS-05-02 specification workers are special classes which handle control or monitoring features for a particular specific device domain.
Different devices will need to use different workers depending on their functionality set.
Indeed, sometimes devices might also need to create vendor specific worker classes (see Vendor specific control classes) either because they implement functionality not catered yet by the standard framework or because they require to derive a standard control class worker.
Context identity mapping (Receiver monitor example)
MS-05-02 specifies an identity mapping mechanism available in the base NcObject class. This touchpoint mechanism can be used to expose and associate identities from outside contexts with entities inside the control structure of the device.
One such example is the ReceiverMonitor control class which is used to express connection and payload statuses for an attached stream receiver.
This allows for a Receiver monitor to be associated with a specific NMOS IS-04 receiver.
A device is expected to offer touchpoints to map identities wherever relevant (For example if the device has a specific worker class like the Receiver monitor which is linked to a resource in another context or specification like an NMOS IS-05 receiver).
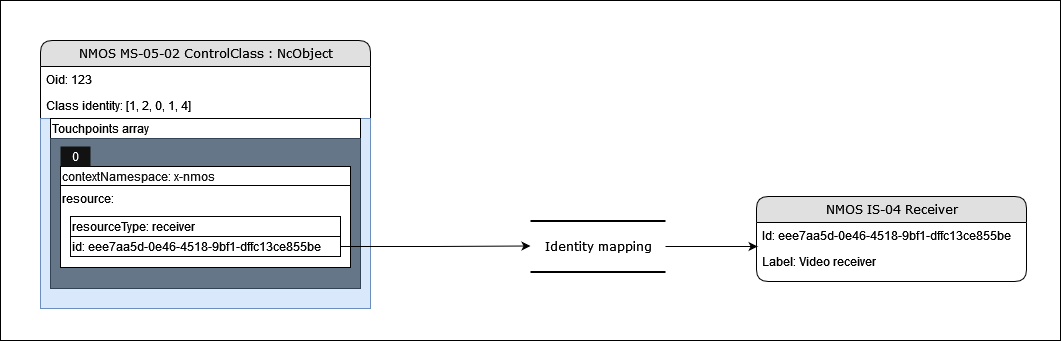 |
|---|
| Context identity mapping |
Minimum requirements
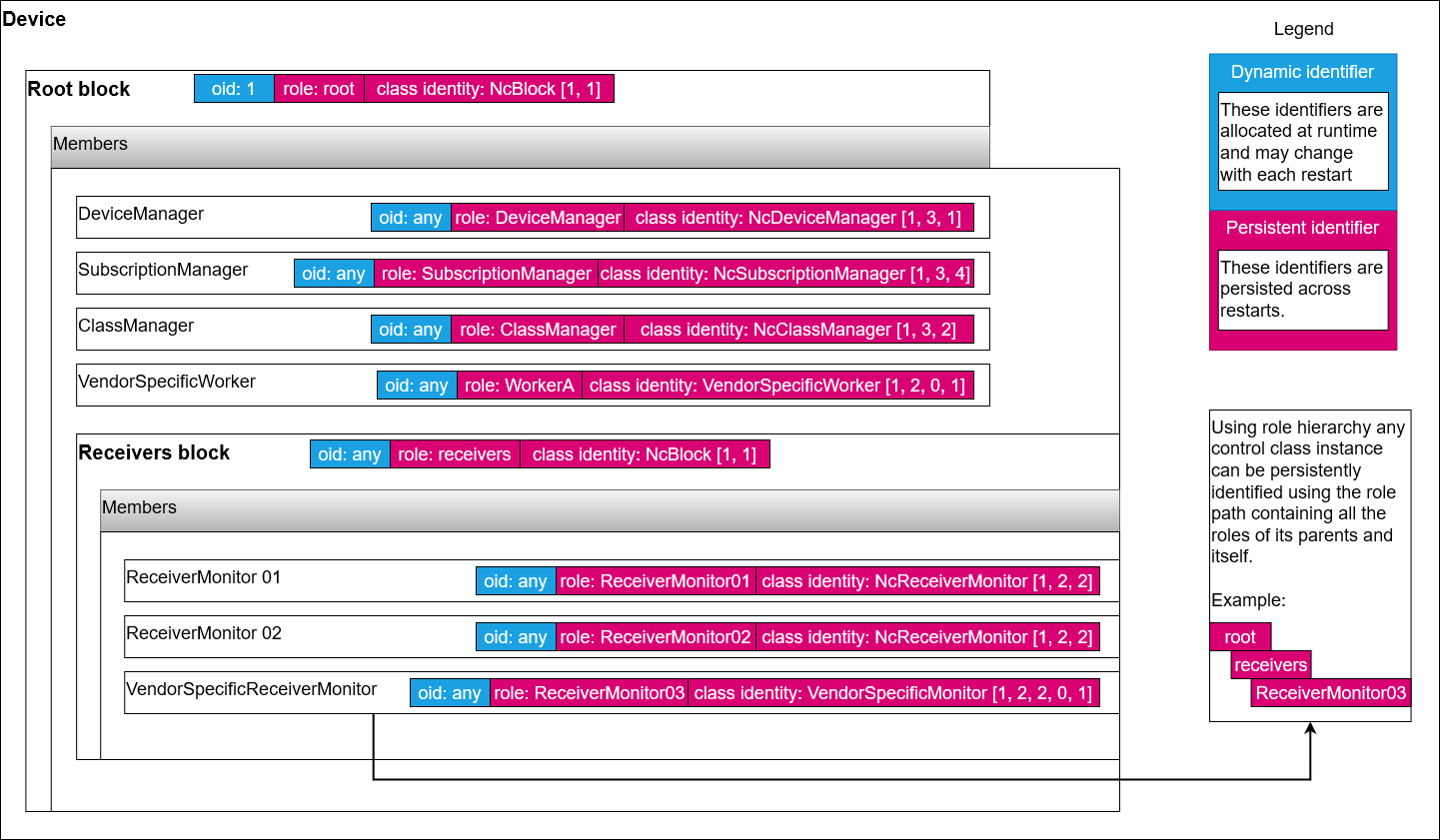
As per the MS-05-02 specification all MS-05 / IS-12 devices need to expose a structure starting with the root block which always has an oid of 1.
A minimal implementation of a device will have at least three managers listed in the root block:
- Device manager
- Subscription manager
- Class manager
 |
|---|
| Typical device structure |
A device is expected to allow its structure to be discovered (see Block control classes) by exposing all of its features in nested blocks starting with the root block.
Vendor specific control classes
Vendor specific control classes can be created by branching off from a standard control class and following the class ID generation guidelines specified in MS-05-01.
Here is an example of a new worker control class called DemoClassAlpha. It inherits from NcWorker which has an identity of [1, 2] and adds the authority key (in this case 0, but should be a negative number if the vendor has an OUI or CID) followed by the index 1.
{
"role": "DemoClassAlpha",
"oid": 111,
"constantOid": true,
"identity": {
"id": [
1,
2,
0,
1
],
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"userLabel": "Demo class alpha",
"owner": 1,
"description": "Demo control class alpha",
"constraints": null
}
A subsequent vendor specific worker would look like this:
{
"role": "DemoClassBeta",
"oid": 150,
"constantOid": true,
"identity": {
"id": [
1,
2,
0,
2
],
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"userLabel": "Demo class beta",
"owner": 1,
"description": "Demo control class beta",
"constraints": null
}
ensuring class identity uniqueness.
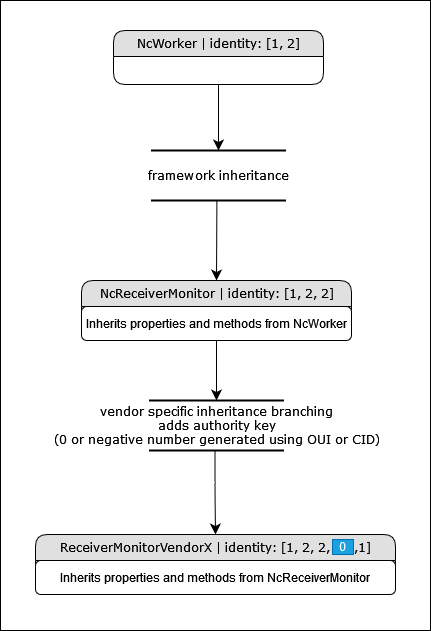 |
|---|
| Vendor specific branching |
Exposing models through the protocol
After a device has initiated its device tree structure and allocated oids to every control class instance, it then either waits for external commands which interact with these entities (e.g. get/set values, invoke actions) or sends notifications for properties which have changed if there are subscribers.
IS-12 defines the protocol messaging behavior but also what the different JSON representations are for specific data types.
Control endpoint advertisement (in NMOS IS-04)
The NMOS IS-12 specification explains that the control endpoint is advertised in the controls array as part of the NMOS device resource. The schema for the NMOS device resource is available in the NMOS IS-04 specification.
It is expected that an IS-12 enabled device exposes a urn:x-nmos:control:ncp control type in the controls array for its NMOS device resource.
Control endpoint example:
{
...
"senders": [
...
],
"receivers": [
...
],
"controls": [
{
"type": "urn:x-nmos:control:ncp/v1.0",
"href": "ws://hostname/example"
}
],
"type": "urn:x-nmos:device:generic",
"id": "58f6b536-ca4c-43fd-880a-9df2501fc125",
...
}
Keeping track of control sessions
As per the NMOS IS-12 specification a device needs to be able to respond to a CreateSession message being received.
The control session provides the control context for subsequent commands, receiving responses and notifications. It also specifies how often heartbeats are sent (see Handling heartbeats).
A device is expected to allocate a session id and offer its value in the response message sent after a valid Create session message is received. This session id will be used in every subsequent communication and the device needs to use it whenever it determines if notifications need to be sent to a specific controller.
Controllers will send the desired heartbeat interval when sending a Create session message. Devices then need to use this interval to validate if heartbeat messages are sent at correct intervals.
Mapping commands and returning responses
As per the NMOS IS-12 specification a device is expected to respond to Commands sent by a controller.
Note: Multiple commands can be sent in the messages array.
As per the MS-05-02 specification all control classes must inherit from NcObject which specifies generic Get and Set methods.
These methods can be used by a controller to get the value of a property in a control class or set the value of a property in a control class if write allowed. Furthermore, any control class may have its own methods which can be invoked in the same way as the generic methods.
As specified by the IDL any method response must inherit from the base data type NcMethodResult.
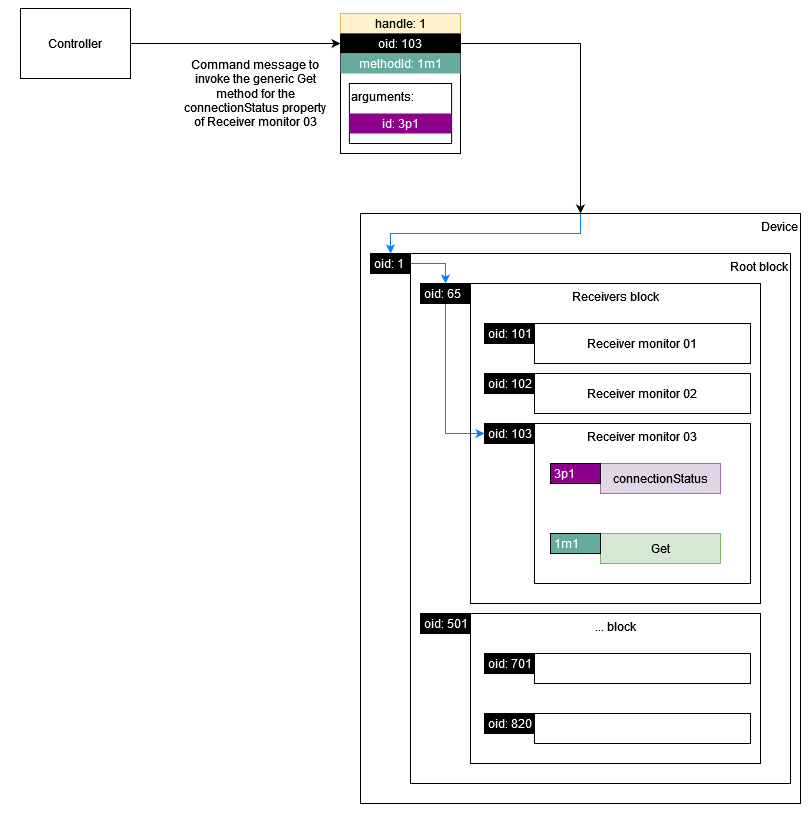 |
|---|
| Command example |
Subscriptions, events and notifications
As per the MS-05-02 specification all control classes must inherit from NcObject which specifies the PropertyChanged event.
This means any properties in any control class can be subscribed to in order to receive change notifications. Subscriptions are handled by the Subscription manager.
A device is expected to allow controllers to Subscribe to object ids it is interested in by correctly handling commands sent to the Subscription manager.
A device is also expected to use the session id context and the subscriptions received in order to determine when a notification message needs to be sent to a controller.
Handling heartbeats
As per the NMOS IS-12 specification a controller is required to send Heartbeat messages for their control sessions at the intervals specified when creating the session (see Keeping track of control sessions).
Devices are expected to acknowledge each heartbeat with a response.
How to
HOW TO practical examples are available here.

