Backup & restore
Supporting backup & restore is a key feature of IS-14. To discuss the various possible combinations of backup and restore, this section utilizes terms explained in the Definitions section.
The Configuration API defines a bulkProperties endpoint which allows:
- Getting all the properties of a role path
- Setting bulk properties for a role path
- Validating bulk properties for a role path
These mechanisms are used for enabling backup and restore functionality and this section of the specification aims to cover the expectations, behaviour and requirements for the following scenarios:
- Performing a backup
- Restoring a full backup data set to a dynamic device after a faulty unit is replaced with an identical spare
- Restoring a full backup data set to a fixed device after a faulty unit is replaced with an identical spare
Note: This does not mean that the backup & restore functionality can only be used in these scenarios.
Definitions
A device, for the purposes of this section, is a physical or logical entity that can be backed up and restored using the procedures described. It may or may not correspond to an IS-04 Device or IS-04 Node.
Backup data set is the set of data retrieved from a device using the backup procedures described. This is represented as an NcBulkValuesHolder object.
Backup validation fingerprint is an optional string in a backup data set that can be used to capture the various versions of the hardware, software and/or firmware that made up a device at the time the backup was performed. The format of the string is defined by the vendor and is opaque to other systems. This could contain information such as:
- Manufacturer key
- Product key
- Software versions
- Hardware revisions
- Backup response hash
- Timestamp
- Whether its a full device model backup or a partial backup
A device model in the context of this specification refers to all the objects and their properties which are exposed in the configuration API.
A full backup is a backup data set that includes all properties for all role paths of a device model. This is achieved by using the /bulkProperties endpoint.
A partial backup is a backup data set that includes only a subset of role paths of a device model. This is achieved by using the /bulkProperties endpoint.
A modified backup is a full backup or partial backup where the backup data set has been modified by a client. Examples of modified backups include: updating values of existing backup data set properties, adding/removing device model role paths from the backup data set.
General concepts
Role path objects within a backup data set contain a boolean property called isRebuildable. If the object is a non-block object isRebuildable means the object can be reconstructed (constructing a fresh object which can accept changes even to its readonly properties). If the object is a block, isRebuildable depicts it can be reconstructed as mentioned in the statement before but also that its members can be added or removed. When a parent block object is not rebuildable but a member child is rebuildable the implication is that the child cannot change its role within that block when being rebuilt through a restore.
The restore mechanism achieved by Setting bulk properties for a role path affects the device model by either rebuilding it or modifying it.
A restore mode of Modify MUST only be allowed to make changes to existing writeable properties of existing device model objects and cannot modify the device model in a structural way (cannot cause the addition or removal of objects from blocks).
A restore mode of Rebuild allows the changes performed through the Modify mode and allows the following additional ones:
- adding new members to rebuildable block objects by constructing new member objects (structural changes)
- removing existing members from rebuildable block objects by deconstructing the member objects (structural changes)
- reconstructing existing objects (constructing fresh objects which can accept changes even to its readonly properties)
In the interest of interoperability even devices with no rebuildable device model objects MUST accept Rebuild restores but only perform the changes in scope for a Modify restore whilst including notices for any changes to readonly properties. Furthermore, performing a Modify restore MUST be possible even when the backup data set contains readonly properties since writeable properties will results in the desired changes being applied and the readonly properties will result in notices in the response returned.
The general pattern for how devices interpret the restore workflow can be explained as follows:
- devices MUST always offer healthy objects in the device model after a restore
- devices MUST attempt to use the backup data set provided first as a pool of information for changing/constructing/deconstructing/reconstructing a particular role path object and if they have all the necessary data they MUST report the restore status as
Ok. - if the backup data set provided doesn’t have the information required for changing/constructing/deconstructing/reconstructing a particular role path object, but the device can fill in the necessary gaps from an internal knowledge store, then they MUST report the restore status as
Okand include properties which have benefited from internal knowledge store data in the notices property asWarningnotices. - if devices cannot find the required information for changing/constructing/deconstructing/reconstructing a particular role path object in either the backup data set provided or an internal knowledge store then they MUST return
Failedas the restore status.
Performing a backup
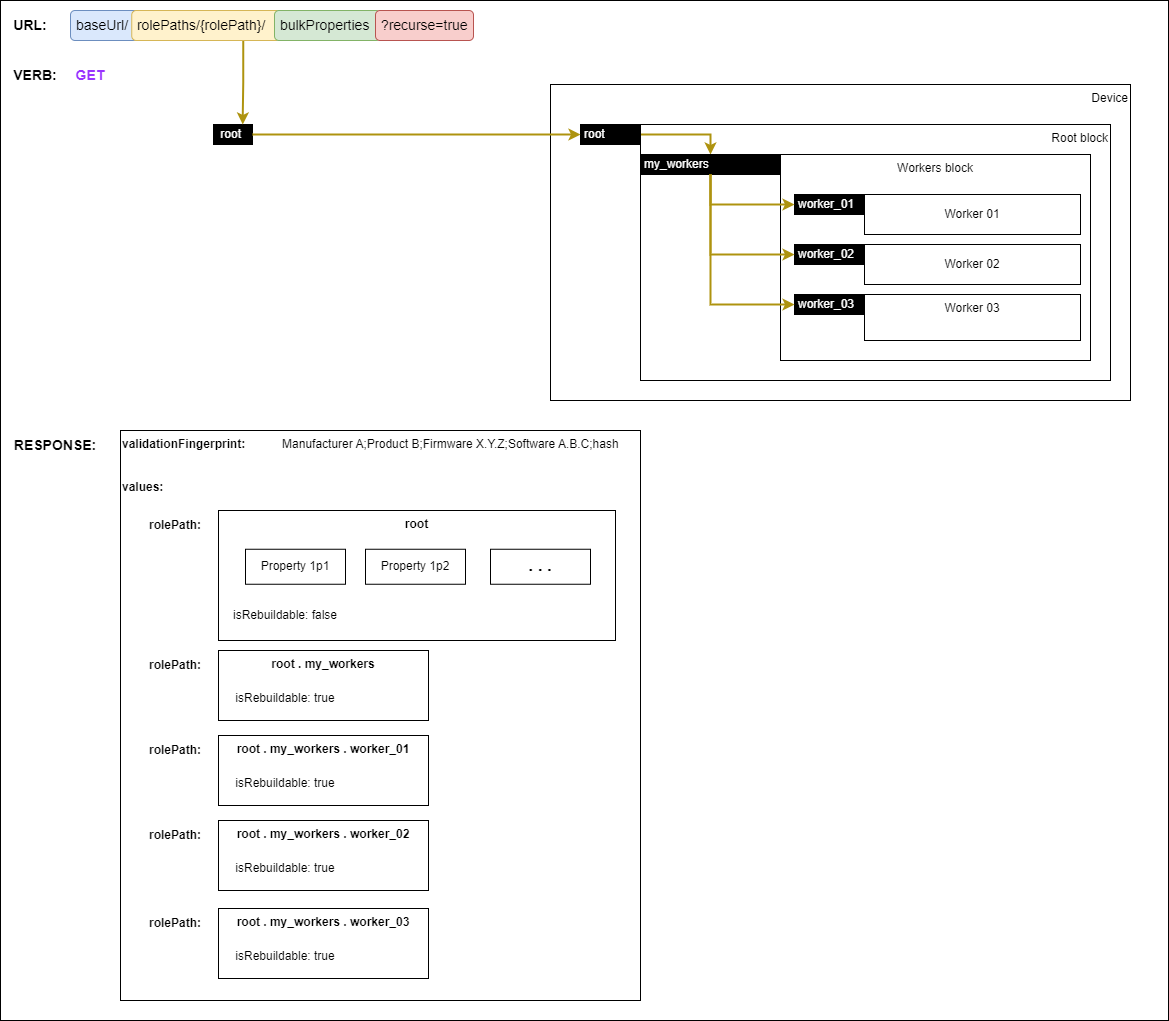
Creating a backup is performed by using the bulkProperties endpoint of a device alongside the Get verb.
In order to retrieve the whole device model (full backup), requests MUST use root as the rolePath. The response contains a validationFingerprint and the values of all the role paths in the device model.
 |
|---|
| Performing a full backup |
Partial backups can be created by choosing other role paths. The scope of backups can further be restricted by using a query parameter of recurse=false which will only include the properties of the targeted role path.
It is RECOMMENDED to store the backup file in its entirety and not remove elements from the data set as they might contain dependencies required by some of the role paths.
Restoring a full backup data set to a dynamic device after a faulty unit is replaced with an identical spare
The following assumptions are made:
- the spare device replacing the faulty unit is the same product type from the same vendor
- a full backup has been created of the faulty unit when it was healthy
- the devices are dynamic containing rebuildable blocks and objects
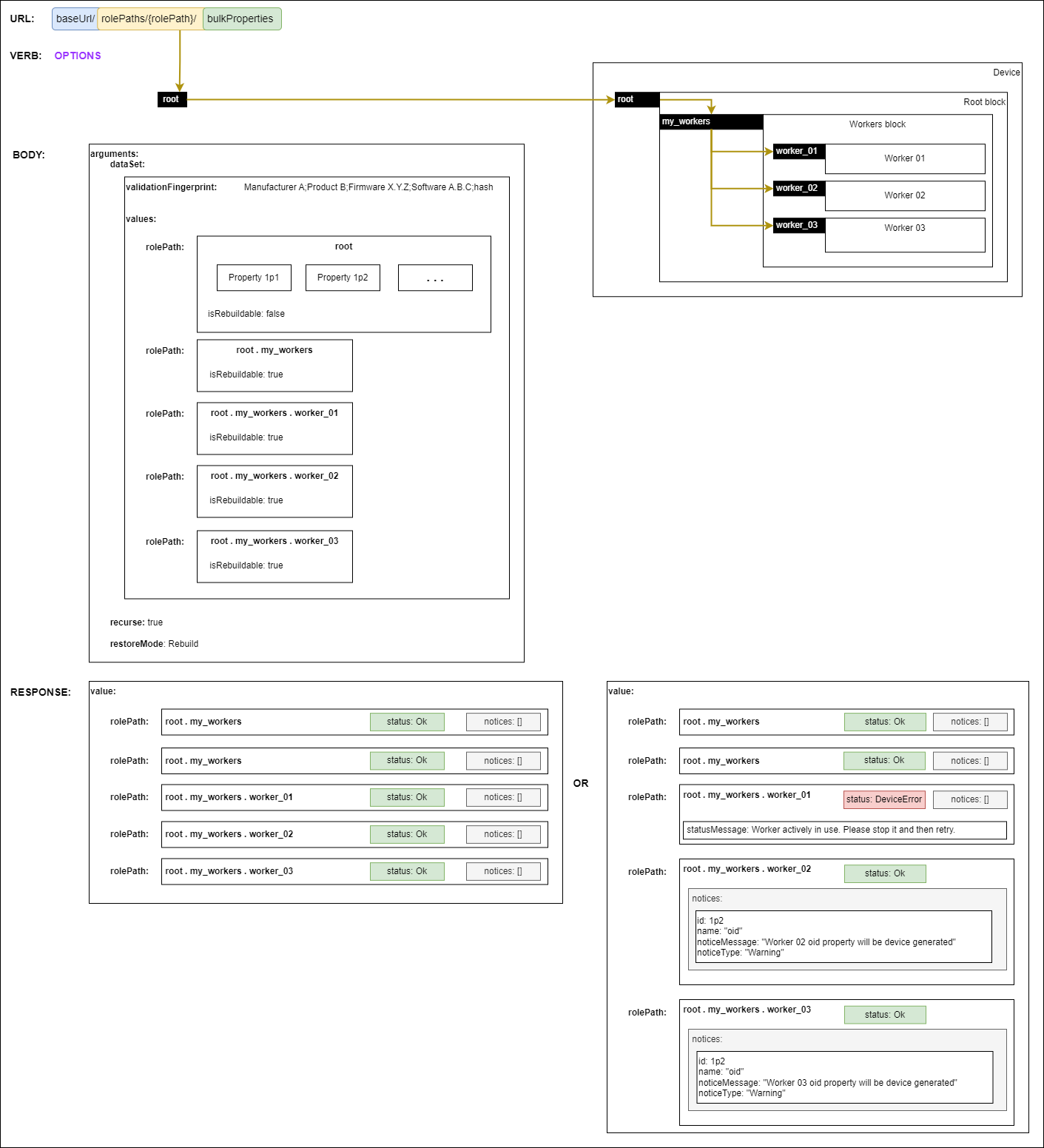
The first step is to perform a Validation request to check if the backup data set can be successfully restored.
In order to validate applying the whole backup data set against the device model, requests MUST use root as the rolePath.
The request body MUST include:
- the backup dataSet
- a boolean
recurseargument (set totruefor validating the whole device model) - the
restoreModeargument (set toRebuildin order to allow blocks to be repopulated with the same members as per the original device)
 |
|---|
| Validating a full backup |
The response MUST include a collection of all target device model role paths with a validation status property and a notices array of property notices. For role paths which have a status which is not a 2XX value the response MUST also include a statusMessage with details of why the validation failed. When there are properties of role path objects which cannot be validated from the values provided in the dataset, these MUST be reported in the notices property as Warning notices.
The backup can be restored by performing a Set request to restore the backup.
In order to use the whole backup data set to restore against the device model, requests MUST use root as the rolePath.
The request body MUST include:
- the backup dataSet
- a boolean
recurseargument (set totruefor validating the whole device model) - the
restoreModeargument (set toRebuildin order to allow blocks to be repopulated with the same members as per the original device)
 |
|---|
| Restoring a full backup |
The response MUST include a collection of all target device model role paths with a validation status property and a notices array of property notices. For role paths which have a status which is not a 2XX value the response MUST also include a statusMessage with details of why the restore failed. When there are properties of role path objects which cannot be restored from the values provided in the dataset, these MUST be reported in the notices property as Warning notices.
If devices require a system reboot in order to apply the restore then they MUST perform this immediately after responding to the restore request.
The diagram below captures how the Rebuild restore uses the backup data set to transition the spare device from its out of the box device model to a state of functionality identical to the original faulty device.
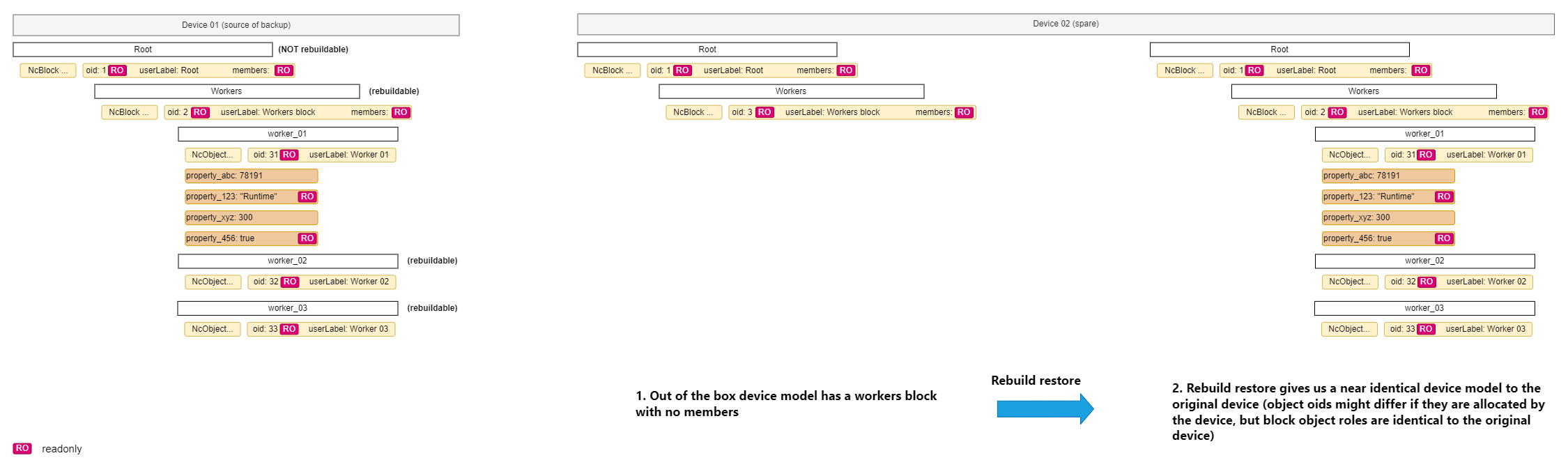 |
|---|
| Rebuild restore of spare |
Restoring a full backup data set to a fixed device after a faulty unit is replaced with an identical spare
The following assumptions are made:
- the spare device replacing the faulty unit is the same product type from the same vendor
- a full backup has been created of the faulty unit when it was healthy
- the devices are fixed containing no rebuildable blocks or objects
The first step is to perform a Validation request to check if the backup data set can be successfully restored.
In order to validate applying the whole backup data set against the device model, requests MUST use root as the rolePath.
The request body MUST include:
- the backup dataSet
- a boolean
recurseargument (set totruefor validating the whole device model) - the
restoreModeargument (set toModifyin order to only allow changes to writeable properties)
The response MUST include a collection of all target device model role paths with a validation status property and a notices array of property notices. For role paths which have a status which is not a 2XX value the response MUST also include a statusMessage with details of why the validation failed. When there are properties of role path objects which cannot be validated from the values provided in the dataset, these MUST be reported in the notices property as Warning notices.
The backup can be restored by performing a Set request to restore the backup.
In order to use the whole backup data set to restore against the device model, requests MUST use root as the rolePath.
The request body MUST include:
- the backup dataSet
- a boolean
recurseargument (set totruefor validating the whole device model) - the
restoreModeargument (set toModifyin order to only allow changes to writeable properties)
The response MUST include a collection of all target device model role paths with a validation status property and a notices array of property notices. For role paths which have a status which is not a 2XX value the response MUST also include a statusMessage with details of why the restore failed. When there are properties of role path objects which cannot be restored from the values provided in the dataset, these MUST be reported in the notices property as Warning notices.
If devices require a system reboot in order to apply the restore then they MUST perform this immediately after responding to the restore request.
The diagram below captures how the Rebuild restore uses the backup data set to transition the spare device from its out of the box device model to a state of functionality identical to the original faulty device.
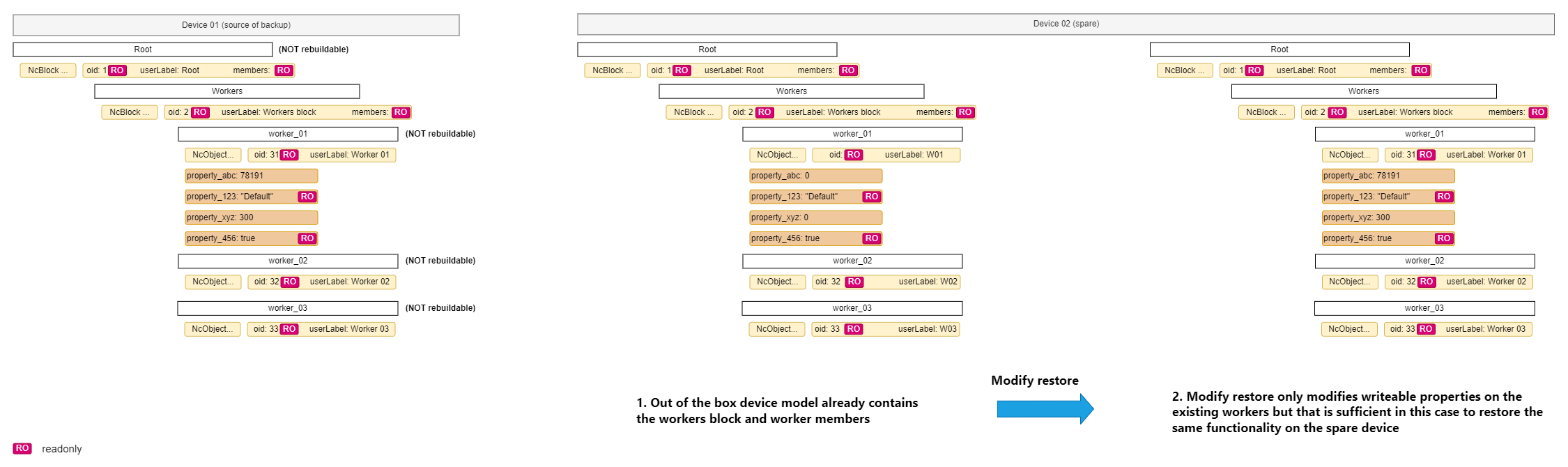 |
|---|
| Modify restore of spare |

